What is GST Registration?
GST Registration is a process where every eligible business gets a 15-digit GSTIN (GST Identification Number). This number identifies your business and allows you to collect taxes and claim Input Tax Credit.
If your business turnover crosses the limit prescribed under GST law, or you sell through online marketplaces, GST registration is mandatory.

Documents Required for GST Registration
Every business that meets the GST eligibility criteria must register to obtain a unique 15-digit GST Identification Number (GSTIN). This number helps the government identify and verify the business.
Below are the updated documents required for GST registration:
Identity & Ownership Documents
- PAN Card of the applicant (Individual/Business/Company)
- Aadhaar Card of the owner/authorized person
- Recent Passport-size Photograph of the Owner / Partner / Director
Business Address Proof
- Any one of the following:
- Electricity bill / Rent agreement
- Property tax receipt
- Lease deed
- NOC from the property owner (if the office is rented)
Business Registration Proof
- Certificate of Incorporation / Business Registration Proof(for Company, LLP, or Partnership Firm)
- Authorization Letter / Board Resolution(if an authorized signatory is applying)
Bank Details
- Bank statement / Passbook
- Cancelled cheque
Additional Requirements
- Digital Signature (DSC) – Required for Company/LLP registrations
- Valid Email ID and Mobile Number for OTP verification

Digital Signature
GST Registration in India – Complete Guide
Online GST registration is now mandatory for businesses operating in India. GST has improved the transparency and efficiency of the tax system. Any business with an annual turnover of ₹40 lakhs or more (₹20 lakhs for some special category states) must apply for GST registration.
Our professional CA team provides hassle-free GST Registration Services along with annual maintenance and return filing support.
What is GST?
GST (Goods and Services Tax) is a comprehensive indirect tax levied on the supply of goods and services across India. It was implemented on 1st July 2017 to replace multiple indirect taxes such as Excise Duty, Service Tax, VAT, Entry Tax, Luxury Tax, etc.
Before GST, businesses had to deal with different taxes at the state and central levels. GST has simplified this system by combining them into one unified tax, making compliance easier for businesses.
Why GST Was Introduced?
GST was introduced to:
✔ Eliminate multiple taxes
✔ Create a uniform market across India
✔ Make business operations easier
✔ Reduce tax evasion and increase transparency
GST (Goods and Services Tax) is a comprehensive indirect tax levied on the supply of goods and services across India. It was implemented on 1st July 2017 to replace multiple indirect taxes such as Excise Duty, Service Tax, VAT, Entry Tax, Luxury Tax, etc.
Before GST, businesses had to deal with different taxes at the state and central levels. GST has simplified this system by combining them into one unified tax, making compliance easier for businesses.
How GST Works?
GST follows a dual tax structure, meaning both the Central and State governments collect tax:
🔹 CGST (Central GST):
Collected by the Central Government on intra-state supply of goods and services.
🔹 SGST (State GST):
Collected by the State Government on intra-state supply of goods and services.
🔹 IGST (Integrated GST):
Collected by the Central Government on inter-state (between states) supply of goods and services.
Types of GST Registrations
🔹 Regular Taxpayer – Normal business, most common
🔹 Composition Scheme – Small businesses, low tax, easy compliance
🔹 Casual Taxable Person – Temporary business (mela/exhibition)
🔹 Non-Resident Taxable Person – Outside India but doing business in India
🔹 Input Service Distributor (ISD) – Head office distributes input tax to branches
🔹 Tax Deductor / Collector – TDS / TCS under GST
🔹 E-Commerce Operator –Platforms like marketplace collect TCS
🔹 OIDAR Services –Online digital services from outside India
Benefits of GST Registration
GST Registration offers multiple advantages for businesses in India. It gives legal recognition to the business, improves credibility, and ensures smooth compliance with tax laws. Registered businesses can claim Input Tax Credit (ITC) on purchases, which helps reduce the overall tax burden.
GST enables inter-state trade without restrictions, making it easier to sell products or services across India. It also allows participation on e-commerce platforms like Amazon, Flipkart, etc. Small businesses can opt for the Composition Scheme, which offers simplified filing and lower tax rates based on turnover.
Overall, GST Registration provides better business opportunities, access to government schemes, easier online selling, and a smooth, transparent tax system.
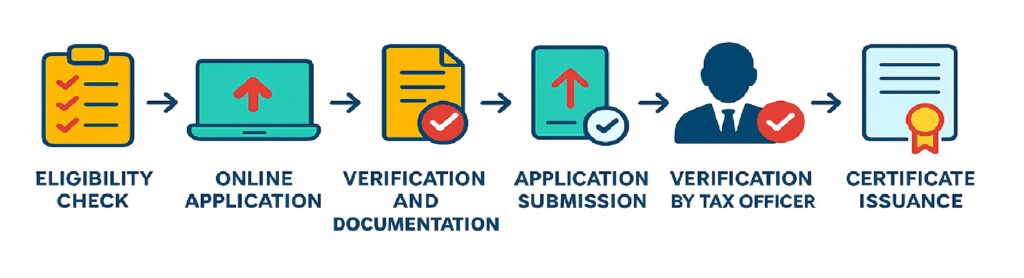
GST Registration Process + What is GSTIN
Step-by-Step GST Registration Process

Confirm whether your business is required to register under GST based on turnover, business type, or interstate supply.

Fill in basic details on the GST portal such as PAN, email, mobile number, business address, etc.

Upload necessary documents like Aadhaar, PAN, address proof, bank details, photographs, and business proof.
✔ Application Submission
Submit the application online. After submission, an Application Reference Number (ARN) is generated.
✔ Officer Verification
A GST officer reviews the application. If any clarification is required, the applicant will be notified.
✔ Certificate Issuance
Once approved, the applicant receives the GST Registration Certificate along with the GSTIN.
Goods and Services Tax Identification Number (GSTIN)
GSTIN is a unique 15-digit identification number issued to a taxpayer after successful GST registration. It links the taxpayer’s PAN and State Code, and is used for all GST-related transactions and filings.
Structure (15 digits)
1. Digits 1–2: State code
2. Digits 3–12: Taxpayer’s PAN
3. Digit 13: Entity code (distinguishes multiple registrations under the same PAN)
4. Digit 14: Default letter “Z”
5. Digit 15: Checksum digit (used for validation)
Why GSTIN matters
 Required for filing GST returns and issuing tax invoices.
Required for filing GST returns and issuing tax invoices.


🔹Ensures transparency and compliance under the GST regime.
Short website snippet / meta description
GSTIN (15-digit) — a unique government-issued identifier linking your PAN and State Code for all GST filings, invoices, and tax communications.
Online vs. Offline GST Registration
Businesses in India can apply for GST registration either online or offline, depending on their convenience and comfort level. Below is a clear comparison of both methods:
Online GST Registration
✔ Convenient & 24/7 Access
Registration can be completed anytime through the GST Common Portal, eliminating the need to visit any office.
✔ Faster Processing
Application submission, document upload, and verification are all done digitally, speeding up the approval process.
✔ Real-Time Tracking
Applicants can check application status, receive notifications, and respond to queries directly on the portal.
✔ Paperless Documentation
All documents are uploaded electronically, reducing paperwork and simplifying the verification process.
✔ Instant Issuance
Once approved, the GSTIN and Registration Certificate are issued online—no physical collection required.
Offline GST Registration
✔ Professional Assistance
Many businesses prefer offline mode to get help from accountants or GST practitioners who manage the entire process.
✔ Face-to-Face Support
Those comfortable with physical interaction can visit the tax office to submit applications and clarify doubts in person.
✔ Local & Regional Preference
In some areas where online access is limited or local habits favor offline work, physical submission may be preferred.

GST Registration Certificate
The GST Registration Certificate is an official document issued by the Government of India after a taxpayer successfully completes the GST registration process. It serves as legal proof that the business is registered under the Goods and Services Tax (GST) system.
The certificate includes important details such as:
- GSTIN (Goods and Services Tax Identification Number)
- Legal name of the business
- Trade name (if any)
- Type of registration
- Constitution of the business
- Date of registration
- Place of business
- Validity and approval status
Every registered taxpayer must keep this certificate accessible, as it is required for compliance, billing, and verification purposes under the GST law.
GST Compliance After Registration
After obtaining GST registration in India, businesses must follow continuous compliance requirements to stay legally valid under the GST law. These compliances ensure proper reporting of sales, purchases, and taxes.
Key compliance obligations include:
 Regular GST Return Filing
Regular GST Return Filing
Businesses must file periodic GST returns such as:
- GSTR-1 – Monthly/quarterly return for outward supplies (sales).
- GSTR-3B – Monthly summary return for sales, purchases, and tax payment.
- GSTR-9 – Annual return summarizing the entire year’s transactions.
 Accurate Record Maintenance
Accurate Record Maintenance
Taxpayers must maintain proper records of invoices, purchase bills, input tax credit (ITC), stock, and financial statements.
 Timely Tax Payment
Timely Tax Payment
Any GST liability must be paid within the due date to avoid interest and penalties.
 Updating Business Information
Updating Business Information
Any changes such as address, business structure, or contact details must be updated on the GST portal.
 Compliance with Notices & Audits
Compliance with Notices & Audits
Businesses must respond to departmental notices and cooperate during GST audits or assessments.
Common GST Registration Issues
During the GST registration process in India, many businesses face common challenges that can delay or complicate their application. Some of the most frequent issues include:
1️⃣ Incorrect or Incomplete Information
Errors in PAN, Aadhaar, business name, address, or contact details often lead to application rejection or delays.
2️⃣ Improper Document Submission
Incorrect, blurred, or missing documents such as address proof, bank details, or business ownership proof cause verification issues.
3️⃣ Technical Glitches on the GST Portal
Server downtime, slow loading, and portal errors frequently interrupt the registration process.
4️⃣ Complex Business Structures
Businesses with branches, multiple owners, or unique setups may face difficulty in providing correct details.
5️⃣ Previous Tax Irregularities
Unresolved tax disputes or mismatched information with the Income Tax database can create registration hurdles.
6️⃣ Incorrect Jurisdiction Selection
Mistakes in choosing the proper state or division office delay the application review.
7️⃣ Delayed Response to Queries
If applicants do not respond to clarification notices on time, the application may be rejected.
8️⃣ Non-Compliance With GST Rules
Failure to meet basic GST requirements or discrepancies in business activity details can lead to rejection.